1. What is the projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of the Waste-to-Energy Plants?
The projected CAGR is approximately 4.6%.
MR Forecast provides premium market intelligence on deep technologies that can cause a high level of disruption in the market within the next few years. When it comes to doing market viability analyses for technologies at very early phases of development, MR Forecast is second to none. What sets us apart is our set of market estimates based on secondary research data, which in turn gets validated through primary research by key companies in the target market and other stakeholders. It only covers technologies pertaining to Healthcare, IT, big data analysis, block chain technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), Energy & Power, Automobile, Agriculture, Electronics, Chemical & Materials, Machinery & Equipment's, Consumer Goods, and many others at MR Forecast. Market: The market section introduces the industry to readers, including an overview, business dynamics, competitive benchmarking, and firms' profiles. This enables readers to make decisions on market entry, expansion, and exit in certain nations, regions, or worldwide. Application: We give painstaking attention to the study of every product and technology, along with its use case and user categories, under our research solutions. From here on, the process delivers accurate market estimates and forecasts apart from the best and most meaningful insights.
Products generically come under this phrase and may imply any number of goods, components, materials, technology, or any combination thereof. Any business that wants to push an innovative agenda needs data on product definitions, pricing analysis, benchmarking and roadmaps on technology, demand analysis, and patents. Our research papers contain all that and much more in a depth that makes them incredibly actionable. Products broadly encompass a wide range of goods, components, materials, technologies, or any combination thereof. For businesses aiming to advance an innovative agenda, access to comprehensive data on product definitions, pricing analysis, benchmarking, technological roadmaps, demand analysis, and patents is essential. Our research papers provide in-depth insights into these areas and more, equipping organizations with actionable information that can drive strategic decision-making and enhance competitive positioning in the market.
 Waste-to-Energy Plants
Waste-to-Energy PlantsWaste-to-Energy Plants by Type (Small and Medium-sized Plants, Large Plants), by Application (Energy Production), by North America (United States, Canada, Mexico), by South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America), by Europe (United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Benelux, Nordics, Rest of Europe), by Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Israel, GCC, North Africa, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), by Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, ASEAN, Oceania, Rest of Asia Pacific) Forecast 2026-2034
The global waste-to-energy (WtE) plant market, valued at $11.72 billion in 2025, is projected to experience robust growth, driven by increasing urbanization, stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing landfill waste, and the escalating need for renewable energy sources. The 4.6% CAGR indicates a steady expansion over the forecast period (2025-2033), with significant contributions expected from both small and medium-sized plants serving municipal needs and large-scale plants catering to industrial waste management. The energy production application segment is a key driver, as WtE plants offer a sustainable solution for electricity generation while addressing waste disposal challenges. Technological advancements, particularly in gasification and pyrolysis, are further enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of WtE technologies, making them more attractive to investors and municipalities. Geographical expansion is also expected, with regions like Asia Pacific, driven by rapid industrialization and population growth in countries like China and India, demonstrating substantial growth potential. However, high initial capital investment costs and potential public resistance based on environmental concerns remain key restraints.


The market segmentation reveals significant opportunities within specific niches. Large-scale WtE plants, though requiring higher upfront investment, offer economies of scale and greater energy production capacity, appealing to larger industrial complexes and municipalities. Smaller plants provide a more localized solution, ideal for smaller communities and regions with limited infrastructure. Regional variations reflect differing waste management policies and infrastructure developments. North America and Europe, with established WtE infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations, are expected to maintain a strong market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is poised for rapid growth, driven by increasing governmental support and investment in renewable energy initiatives. This growth will likely be fueled by increasing awareness of environmental sustainability and the need for efficient waste management solutions.
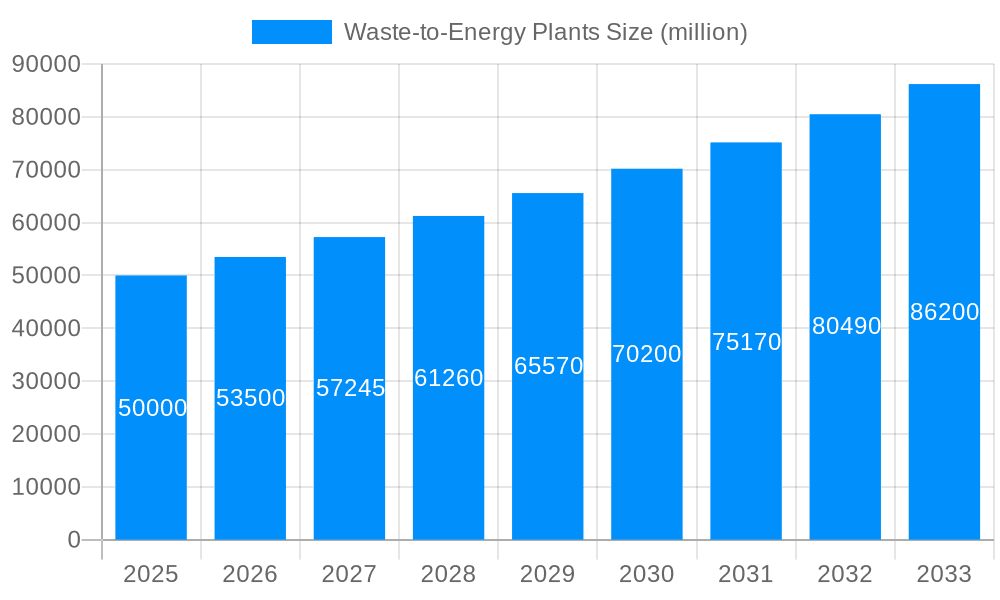

The waste-to-energy (WtE) plant market in China, analyzed over the study period 2019-2033, exhibits robust growth, driven by escalating waste generation and stringent environmental regulations. The market's value is projected to reach several billion USD by 2033, a significant increase from its valuation in 2025. The historical period (2019-2024) witnessed considerable investment in WtE infrastructure, primarily focusing on large-scale plants due to their economies of scale. However, the forecast period (2025-2033) will see a more balanced approach, with growth in both large and small-to-medium sized plants. This shift reflects a strategic diversification to address the diverse waste management needs of different regions and population densities. Small and medium-sized plants are gaining traction due to their flexibility and suitability for smaller municipalities and regions where large-scale projects are not economically feasible. The application segment is predominantly focused on energy production, aiming to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote renewable energy sources. However, industrial applications, such as the utilization of waste-derived materials in manufacturing processes, are also expected to gain prominence in the coming years. This trend is supported by government initiatives promoting circular economy models and the reduction of industrial waste. The market’s dynamic nature is shaped by technological advancements in waste processing, improved efficiency in energy recovery, and evolving regulatory frameworks that incentivize sustainable waste management practices. Key market insights indicate a significant increase in private sector participation, attracting considerable foreign direct investment and fostering innovation within the industry. The increasing awareness of environmental sustainability, coupled with economic incentives, is further solidifying the position of WtE plants as a crucial component of China's comprehensive waste management strategy. The base year 2025 provides a crucial benchmark for assessing the market's trajectory and evaluating the effectiveness of various governmental policies in promoting the industry's growth and development.
Several key factors are driving the rapid expansion of the waste-to-energy plant market in China. Stringent government regulations aimed at reducing landfill waste and promoting renewable energy sources are creating a favorable environment for investment and development. The increasing volume of municipal solid waste (MSW) necessitates innovative solutions, with WtE plants offering a sustainable alternative to traditional landfills. These plants significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to landfills, aligning with China's national commitment to climate change mitigation. Furthermore, the economic viability of WtE plants, particularly in energy-intensive regions, is a strong incentive for their adoption. The generation of renewable energy from waste materials creates a revenue stream, reducing the overall cost of waste management. Technological advancements are also improving the efficiency and environmental performance of WtE plants. Advances in gasification, pyrolysis, and other thermal treatment technologies are enhancing energy recovery rates and minimizing the environmental impact. The integration of advanced air pollution control systems is addressing concerns about emissions, ensuring the plants operate sustainably and comply with increasingly stringent environmental standards. Finally, growing public awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable waste management practices contributes significantly to the increased demand for WtE solutions. This translates to increased social acceptance and support for the development of new WtE infrastructure projects across various regions of China.
Despite the significant growth potential, the WtE sector faces challenges. High capital costs associated with constructing and commissioning large-scale plants remain a significant barrier to entry for smaller companies. Securing financing for these projects can be complex, particularly in the context of long-term investment and uncertain energy markets. The fluctuating prices of fossil fuels can impact the economic viability of WtE plants, making long-term investment planning more difficult. Furthermore, public perception and potential NIMBYism (Not In My Back Yard) remain a concern in some communities. Concerns about potential air pollution, even with advanced emission control technologies, can lead to resistance to new plant construction. Efficient and sustainable waste collection and sorting systems are essential for optimal WtE plant performance. Inconsistent waste streams and contamination can impact the quality of energy produced and reduce overall plant efficiency. Technological limitations and the need for continuous innovation to improve energy recovery rates and reduce environmental impact pose ongoing challenges. Finally, the regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, requiring plant operators to adapt to changing environmental standards and compliance requirements. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, involving government support, technological innovation, and effective public engagement strategies.
The key segment poised for dominance within the Chinese WtE market is Large Plants within the Energy Production application.
Large Plants: Economies of scale make large plants more economically viable, leading to significant investment in their construction. These plants benefit from higher energy recovery rates and optimized operational efficiencies, making them more attractive to investors and government agencies. Their capacity to process larger volumes of waste makes them particularly important in high-population density areas.
Energy Production: The primary application for WtE plants continues to be energy generation. This segment aligns directly with China's national goals to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote renewable energy. The energy produced from waste can be integrated into the national grid, providing a significant contribution to the country's overall energy supply. This application also offers economic incentives for plant operators and contributes to national energy security.
The geographic regions expected to witness the fastest growth in WtE plant capacity are major metropolitan areas and industrialized provinces, driven by the concentration of waste generation and high energy demand. This includes regions like the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. These areas face intense pressure to manage increasing waste volumes while meeting stringent environmental standards. The large scale of waste generation in these regions makes the adoption of large WtE plants a more logical and efficient solution. Further, these regions generally have better infrastructure and access to capital, which accelerates project development and deployment. Government policies focusing on waste management and renewable energy targets within these densely populated regions act as significant growth catalysts. The scale and infrastructure capabilities in these regions help support the operational efficiency of large plants and the reliable integration of generated energy into existing grids. Investment in supporting technologies, such as waste sorting and pretreatment facilities, further complements the effectiveness of large WtE plants in these areas.
Several factors are catalyzing the growth of the WtE industry in China. Government policies promoting renewable energy and sustainable waste management are key drivers. Financial incentives, tax breaks, and subsidies are actively attracting investment in the sector. Technological advancements in waste processing and energy recovery are enhancing the efficiency and environmental performance of WtE plants. The increasing public awareness of environmental issues and the benefits of sustainable waste management is creating a more receptive environment for new projects. Finally, the growing collaboration between government, private sector, and research institutions fosters innovation and accelerates the adoption of advanced technologies.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Chinese waste-to-energy market, covering historical trends, current market dynamics, and future projections. It examines key market drivers, challenges, and growth opportunities, while providing detailed insights into leading companies, prominent projects, and significant technological advancements. The report offers valuable information for investors, policymakers, and industry professionals seeking to understand and participate in this rapidly evolving market. The detailed segmentation by plant size and application allows for a granular understanding of market trends and growth prospects across different sub-sectors.


| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2020-2034 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Estimated Year | 2026 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.6% from 2020-2034 |
| Segmentation |
|




Note*: In applicable scenarios
Primary Research
Secondary Research

Involves using different sources of information in order to increase the validity of a study
These sources are likely to be stakeholders in a program - participants, other researchers, program staff, other community members, and so on.
Then we put all data in single framework & apply various statistical tools to find out the dynamic on the market.
During the analysis stage, feedback from the stakeholder groups would be compared to determine areas of agreement as well as areas of divergence
The projected CAGR is approximately 4.6%.
Key companies in the market include China Everbright, China Energy Conservation and Environment Protection (CECEC), China Renewable Energy (CRE), .
The market segments include Type, Application.
The market size is estimated to be USD 11720 million as of 2022.
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Pricing options include single-user, multi-user, and enterprise licenses priced at USD 3480.00, USD 5220.00, and USD 6960.00 respectively.
The market size is provided in terms of value, measured in million.
Yes, the market keyword associated with the report is "Waste-to-Energy Plants," which aids in identifying and referencing the specific market segment covered.
The pricing options vary based on user requirements and access needs. Individual users may opt for single-user licenses, while businesses requiring broader access may choose multi-user or enterprise licenses for cost-effective access to the report.
While the report offers comprehensive insights, it's advisable to review the specific contents or supplementary materials provided to ascertain if additional resources or data are available.
To stay informed about further developments, trends, and reports in the Waste-to-Energy Plants, consider subscribing to industry newsletters, following relevant companies and organizations, or regularly checking reputable industry news sources and publications.